Подключение кластера Kubernetes (SaaS)⚓︎
Cloudmaster работает
с кластерами
Yandex Managed Service for Kubernetes .
Содержание
Предварительные требования⚓︎
-
Убедитесь, что вы используете одну из версий Kubernetes: 1.28 - 1.31.
-
Вам потребуются:
-
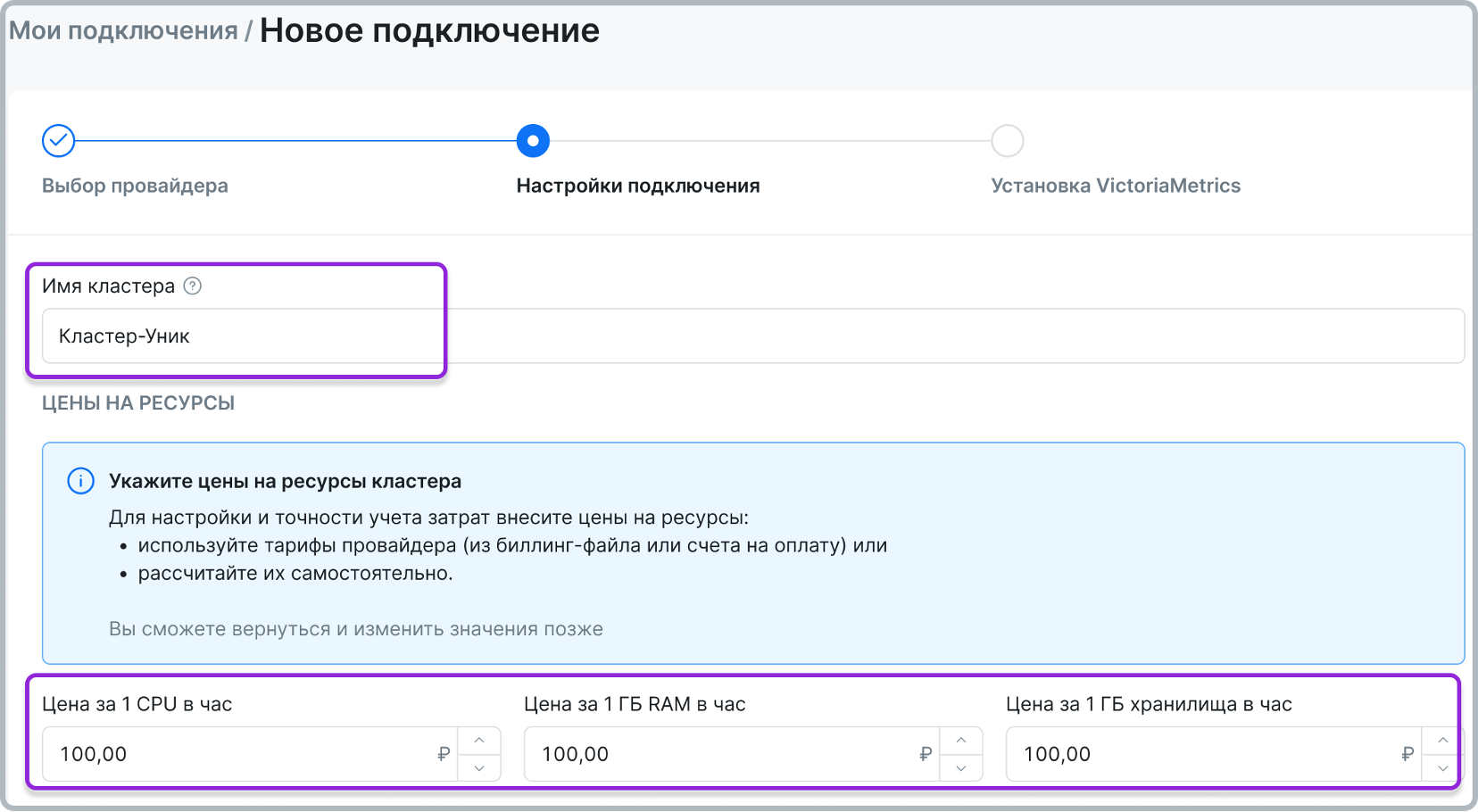
данные о ценах на CPU, RAM и диск для вашего кластера,
-
права на установку kube-state-metrics, node-exporter и агента VictoriaMetrics в ваш кластер.
-
Основные шаги подключения⚓︎
-
В разделе Мои подключения нажмите на кнопку Новое подключение и затем ― на карточку Кластер Kubernetes.
-
В открывшейся форме введите параметры подключения.
Если в какой-то момент вам потребуется закрыть окно подключения, вы сможете вернуться к редактированию черновика.
-
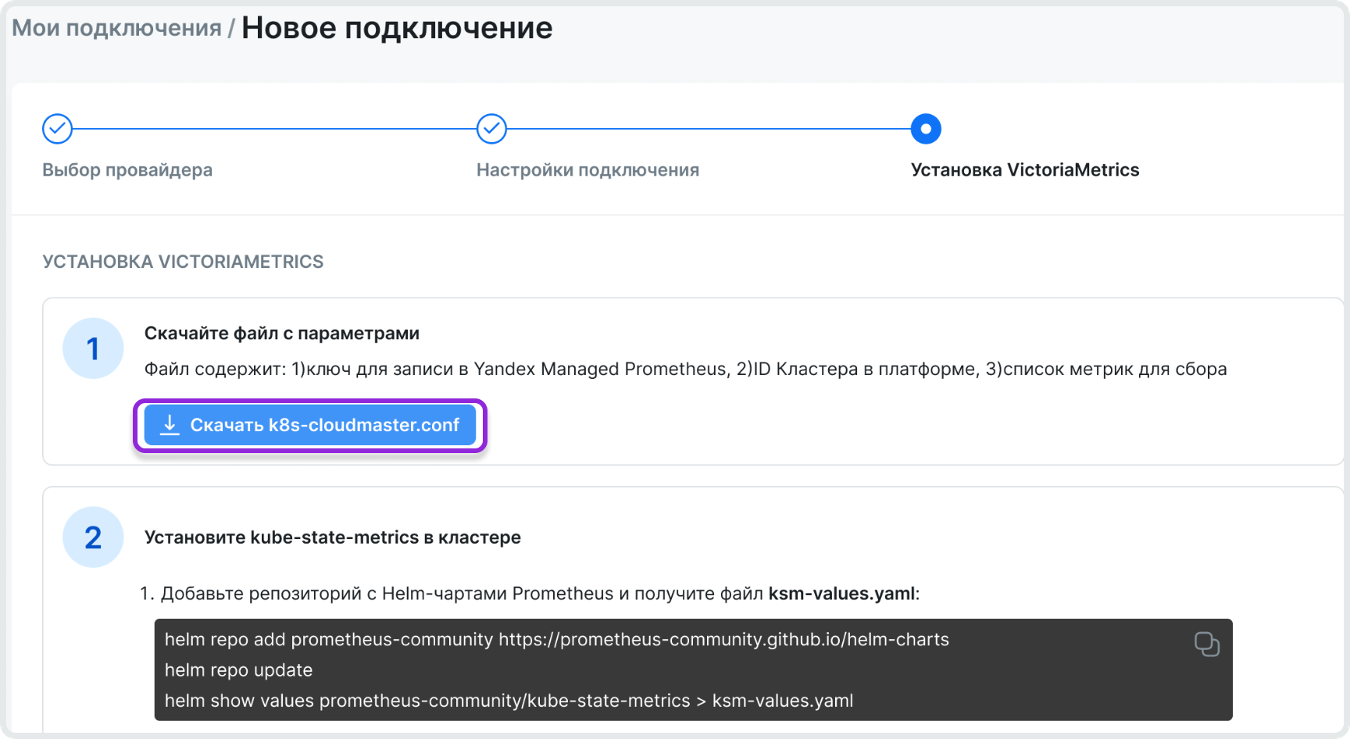
Нажмите на кнопку Далее. Перейдите на шаг установки и настройки VictoriaMetrics.
-
Ознакомьтесь с инструкцией по настройке kube-state-metrics, node-exporter и VictoriaMetrics. Инструкция продублирована ниже в этой статье.
-
После ознакомления с инструкцией кликните на Скачать k8s-cloudmaster.conf, чтобы получить файл с параметрами кластера.
-
Выполните шаги инструкции и проверьте результат.
-
Кликните Создать. Кнопка станет активной только после скачивания файла k8s-cloudmaster.conf.
-
После завершения работы визарда подключение кластера появится на странице Мои подключения.
Начальный статус кластера Неактивно. Сбор начальных данных займет около 30 минут. Проверьте статус кластера в Мои подключения и данные по затратам в разделе Kubernetes. Рекомендации отобразятся после накопления данных за 7 дней.
Где хранятся данные кластера
Метрики кластера Kubernetes для SaaS-версии продукта будут отправляться в
Yandex Managed Service for Prometheus по
протоколу
Remote-Write
Установка kube-state-metrics⚓︎
Сервис kube-state-metrics — сервис, который прослушивает API-сервер Kubernetes и генерирует метрики о состоянии различных объектов Kubernetes.
Если у вас уже установлен kube-state-metrics, проверьте активные коллекторы по списку ниже и перейдите к следующему шагу.
-
Добавьте репозиторий с Helm-чартами Prometheus и получите значения по умолчанию для kube-state-metrics с помощью команд:
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts helm repo update helm show values prometheus-community/kube-state-metrics > ksm-values.yamlВы получите файл ksm-values.yaml с параметрами kube-state-metrics по умолчанию.
-
В полученном файле ksm-values.yaml отредактируйте блок collectors, закомментируйте все коллекторы, кроме списка ниже.
Блок должен выглядеть так:
-
Установите сервис kube-state-metrics в
кластерс помощью команды: -
Приступите к следующему шагу.
Уcтановка node-exporter⚓︎
Сервис node-exporter — это инструмент (или "экспортер" метрик), который собирает системные метрики с серверов (узлов) и предоставляет их в формате, понятном для Prometheus или Victoria Metrics. В Kubernetes node-exporter разворачивается как DaemonSet. Это гарантирует, что на каждом узле кластера будет работать по одному экземпляру node-exporter.
-
Создайте файл node-exporter-daemonset.yaml со следующим содержанием.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: node-exporter namespace: cloudmaster-vm labels: app: node-exporter spec: selector: matchLabels: app: node-exporter template: metadata: labels: app: node-exporter spec: hostNetwork: true hostPID: true containers: - name: node-exporter image: quay.io/prometheus/node-exporter:v1.6.1 ports: - containerPort: 9100 hostPort: 9100 protocol: TCP volumeMounts: - name: proc mountPath: /host/proc readOnly: true - name: sys mountPath: /host/sys readOnly: true args: - '--path.procfs=/host/proc' - '--path.sysfs=/host/sys' volumes: - name: proc hostPath: path: /proc - name: sys hostPath: path: /sys -
Установите node-exporter с помощью команды:
Установка ВМ-агента VictoriaMetrics⚓︎
Агент VictoriaMetrics будет временно хранить и отправлять данные по метрикам в кластере.
Инструкция по установке ВМ-агента VictoriaMetrics⚓︎
-
Настройте helm на подключение к
кластеруKubernetes. -
Добавьте helm-репозиторий с помощью команд:
helm repo add victoria-metrics https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts/ helm repo update helm show values victoria-metrics/victoria-metrics-agent > vma-values.yamlВы получите файл vma-values.yaml с параметрами по умолчанию.
-
Откройте файл k8s-cloudmaster.conf и скопируйте значения.
Далее мы будем редактировать файл vma-values.yaml . Важно! Удалять из файла ничего не нужно, только добавлять и менять.
-
В файле vma-values.yaml
Измените следующие значения:
-
API-ключ,
-
ID
кластера, -
список метрик.
Фрагмент файла для редактирования:
remoteWrite: - url: "https://metrics.cloudmaster.ru/metrics/write" forcePromProto: true headers: "Authorization: Api-Key ЗНАЧЕНИЕ_API_КЛЮЧА" urlRelabelConfig: - action: replace replacement: 'ID_КЛАСТЕРА' target_label: cluster - action: keep source_labels: ['__name__'] regex: 'container_cpu_usage_seconds_total|container_memory_working_set_bytes|kube_pod_container_resource_requests|container_fs_limit_bytes|kube_persistentvolume_capacity_bytes' -
-
В блоке config файла vma-values.yaml только ДОБАВЛЯЕМ И ИЗМЕНЯЕМ (значения по умолчанию сохраняем, ничего удалять не нужно).
Измените scrape_interval на 60, добавьте в scrape_configs джобы: kube-state-metrics и node-exporter:
config: global: scrape_interval: 60s scrape_configs: - job_name: kube-state-metrics kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name] regex: kube-state-metrics action: keep - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number] regex: "8080" action: keep - job_name: node-exporter kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '(.*):10250' replacement: '${1}:9100' target_label: __address__ -
Проверьте содержание получившегося конфигурационного файла. Ниже приведен пример полного файла после внесения изменений. Особенно обратите внимание, что в файле присутствует джоба kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor.
Пример полного файла vma-values.yaml
# Default values for victoria-metrics-agent. # This is a YAML-formatted file. # Declare variables to be passed into your templates. global: # -- Image pull secrets, that can be shared across multiple helm charts imagePullSecrets: [] image: # -- Image registry, that can be shared across multiple helm charts registry: "" # -- Openshift security context compatibility configuration compatibility: openshift: adaptSecurityContext: "auto" cluster: # -- K8s cluster domain suffix, uses for building storage pods' FQDN. Details are [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/dns-custom-nameservers/) dnsDomain: cluster.local. # -- Replica count replicaCount: 1 # -- Specify pod lifecycle lifecycle: {} # -- Use an alternate scheduler, e.g. "stork". Check details [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-multiple-schedulers/) schedulerName: "" # -- VMAgent mode: daemonSet, deployment, statefulSet mode: deployment # -- [K8s DaemonSet](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/daemonset/) specific variables daemonSet: spec: {} # -- [K8s Deployment](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/) specific variables deployment: spec: # -- Deployment strategy. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/#strategy) for details strategy: {} # rollingUpdate: # maxSurge: 25% # maxUnavailable: 25% # type: RollingUpdate # -- [K8s StatefulSet](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/statefulset/) specific variables statefulSet: # -- create cluster of vmagents. Check [here](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/vmagent/#scraping-big-number-of-targets) # available since [v1.77.2](https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/VictoriaMetrics/releases/tag/v1.77.2) clusterMode: false # -- replication factor for vmagent in cluster mode replicationFactor: 1 spec: # -- StatefulSet update strategy. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/statefulset/#update-strategies) for details. updateStrategy: {} # type: RollingUpdate image: # -- Image registry registry: "" # -- Image repository repository: victoriametrics/vmagent # -- Image tag, set to `Chart.AppVersion` by default tag: "" # rewrites Chart.AppVersion # -- Variant of the image to use. # e.g. enterprise, scratch variant: "" # -- Image pull policy pullPolicy: IfNotPresent # -- Image pull secrets imagePullSecrets: [] # -- Add additional DNS entries to pods hosts file. Check [official documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/network/customize-hosts-file-for-pods/) hostAliases: [] # - ip: 192.168.1.1 # hostNames: # - test.example.com # - another.example.net # -- Override chart name nameOverride: "" # -- Override resources fullname fullnameOverride: "" # -- Container working directory containerWorkingDir: "/" rbac: # -- Enables Role/RoleBinding creation create: true # -- Role/RoleBinding annotations annotations: {} # -- Role/RoleBinding labels extraLabels: {} # -- If true and `rbac.enabled`, will deploy a Role/RoleBinding instead of a ClusterRole/ClusterRoleBinding namespaced: false # -- additional rules for a role extraRules: [] serviceAccount: # -- Specifies whether a service account should be created create: true # -- Annotations to add to the service account annotations: {} # -- The name of the service account to use. # If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template name: # -- mount API token to pod directly automountToken: true # -- See `kubectl explain poddisruptionbudget.spec` for more or check [official documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/configure-pdb/) podDisruptionBudget: enabled: false # minAvailable: 1 # maxUnavailable: 1 labels: {} # -- Generates `remoteWrite.*` flags and config maps with value content for values, that are of type list of map. # Each item should contain `url` param to pass validation. remoteWrite: - url: "https://metrics.cloudmaster.ru/metrics/write" forcePromProto: true headers: "Authorization: Api-Key Api-Key ЗНАЧЕНИЕ_API_КЛЮЧА" urlRelabelConfig: - action: replace replacement: 'ID_КЛАСТЕРА' target_label: cluster - action: keep source_labels: ['__name__'] regex: 'container_cpu_usage_seconds_total|container_memory_working_set_bytes|kube_pod_container_resource_requests|container_fs_limit_bytes|kube_persistentvolume_capacity_bytes' # -- VMAgent extra command line arguments extraArgs: envflag.enable: true envflag.prefix: VM_ loggerFormat: json httpListenAddr: :8429 # promscrape.maxScrapeSize: "167772160" # Uncomment and specify the port if you want to support any of the protocols: # https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/vmagent/#features # graphiteListenAddr: ":2003" # influxListenAddr: ":8189" # opentsdbHTTPListenAddr: ":4242" # opentsdbListenAddr: ":4242" # -- Additional environment variables (ex.: secret tokens, flags). Check [here](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/#environment-variables) for more details. env: [] # - name: VM_remoteWrite_basicAuth_password # valueFrom: # secretKeyRef: # name: auth-secret # key: password # -- Specify alternative source for env variables envFrom: [] #- configMapRef: # name: special-config # -- Extra labels for Deployment and Statefulset extraLabels: {} # -- Extra labels for Pods only podLabels: {} # -- Additional hostPath mounts extraHostPathMounts: [] # - name: certs-dir # mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs # subPath: "" # hostPath: /etc/kubernetes/certs # readOnly: true # -- Extra Volumes for the pod extraVolumes: [] # - name: example # configMap: # name: example # -- Extra Volume Mounts for the container extraVolumeMounts: [] # - name: example # mountPath: /example # -- Extra containers to run in a pod with vmagent extraContainers: [] # - name: config-reloader # image: reloader-image # -- Init containers for vmagent initContainers: [] # - name: example # image: example-image # -- Security context to be added to pod podSecurityContext: enabled: true # fsGroup: 2000 # -- Security context to be added to pod's containers securityContext: enabled: true # capabilities: # drop: # - ALL # readOnlyRootFilesystem: true # runAsNonRoot: true # runAsUser: 1000 service: # -- Enable agent service enabled: false # -- Service annotations annotations: {} # -- Service labels extraLabels: {} # -- Service ClusterIP clusterIP: "" # -- Service external IPs. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#external-ips) for details externalIPs: [] # -- Service load balancer IP loadBalancerIP: "" # -- Load balancer source range loadBalancerSourceRanges: [] # -- Service port servicePort: 8429 # -- Target port targetPort: http # nodePort: 30000 # -- Service type type: ClusterIP # -- Service IP family policy. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/dual-stack/#services) for details. ipFamilyPolicy: "" # -- List of service IP families. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/dual-stack/#services) for details. ipFamilies: [] # -- Service external traffic policy. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/create-external-load-balancer/#preserving-the-client-source-ip) for details externalTrafficPolicy: "" # -- Service internal traffic policy. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#internal-traffic-policy) for details internalTrafficPolicy: "" # -- Health check node port for a service. Check [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/create-external-load-balancer/#preserving-the-client-source-ip) for details healthCheckNodePort: "" # -- Traffic Distribution. Check [Traffic distribution](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#traffic-distribution) trafficDistribution: "" ingress: # -- Enable deployment of ingress for agent enabled: false # -- Ingress annotations annotations: {} # kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx # kubernetes.io/tls-acme: 'true' # -- Ingress extra labels extraLabels: {} # -- Array of host objects hosts: - name: vmagent.local path: - / port: http # -- Array of TLS objects tls: [] # - secretName: vmagent-ingress-tls # hosts: # - vmagent.local # -- Ingress controller class name ingressClassName: "" # -- Ingress path type pathType: Prefix # -- Resource object. Details are [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/) resources: {} # We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious # choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little # resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following # lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'. # limits: # cpu: 100m # memory: 128Mi # requests: # cpu: 100m # memory: 128Mi # -- Annotations to be added to the deployment annotations: {} # -- Annotations to be added to pod podAnnotations: {} # -- Pod's node selector. Details are [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/assign-pod-node/#nodeselector) nodeSelector: {} # -- Node tolerations for server scheduling to nodes with taints. Details are [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/) tolerations: [] # -- Pod topologySpreadConstraints topologySpreadConstraints: [] # - maxSkew: 1 # topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule # -- Pod affinity affinity: {} # -- VMAgent [scraping configuration](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/vmagent/#how-to-collect-metrics-in-prometheus-format) # use existing configmap if specified # otherwise .config values will be used configMap: "" # -- Priority class to be assigned to the pod(s) priorityClassName: "" serviceMonitor: # -- Enable deployment of Service Monitor for server component. This is Prometheus operator object enabled: false # -- Service Monitor labels extraLabels: {} # -- Service Monitor annotations annotations: {} # -- Service Monitor relabelings relabelings: [] # -- Basic auth params for Service Monitor basicAuth: {} # -- Service Monitor metricRelabelings metricRelabelings: [] # -- Service Monitor targetPort targetPort: http # interval: 15s # scrapeTimeout: 5s # -- Commented. HTTP scheme to use for scraping. # scheme: https # -- Commented. TLS configuration to use when scraping the endpoint # tlsConfig: # insecureSkipVerify: true # -- Empty dir configuration for a case, when persistence is disabled emptyDir: {} persistentVolume: # -- Create/use Persistent Volume Claim for server component. Empty dir if false enabled: false # -- Override Persistent Volume Claim name name: "" # -- StorageClass to use for persistent volume. Requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true. If defined, PVC created automatically storageClassName: "" # -- Array of access modes. Must match those of existing PV or dynamic provisioner. Details are [here](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/persistent-volumes/) accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce # -- Size of the volume. Should be calculated based on the logs you send and retention policy you set. size: 10Gi # -- Persistent volume annotations annotations: {} # -- Persistent volume additional labels extraLabels: {} # -- Existing Claim name. If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound existingClaim: "" # -- Bind Persistent Volume by labels. Must match all labels of targeted PV. matchLabels: {} # -- Horizontal Pod Autoscaling. # Note that it is not intended to be used for vmagents which perform scraping. # In order to scale scraping vmagents check [here](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/vmagent/#scraping-big-number-of-targets) horizontalPodAutoscaling: # -- Use HPA for vmagent enabled: false # -- Maximum replicas for HPA to use to to scale vmagent maxReplicas: 10 # -- Minimum replicas for HPA to use to scale vmagent minReplicas: 1 # -- Metric for HPA to use to scale vmagent metrics: [] # -- VMAgent scrape configuration config: # -- Enable config templating useTpl: false global: scrape_interval: 60s scrape_configs: - job_name: kube-state-metrics kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name] regex: kube-state-metrics action: keep - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number] regex: "8080" action: keep - job_name: "node-exporter" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] regex: '(.*):10250' replacement: '${1}:9100' target_label: __address__ - job_name: vmagent static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:8429"] ## COPY from Prometheus helm chart https://github.com/helm/charts/blob/master/stable/prometheus/values.yaml # Scrape config for API servers. # # Kubernetes exposes API servers as endpoints to the default/kubernetes # service so this uses `endpoints` role and uses relabelling to only keep # the endpoints associated with the default/kubernetes service using the # default named port `https`. This works for single API server deployments as # well as HA API server deployments. - job_name: "kubernetes-apiservers" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpoints # Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to # `http`. scheme: https # This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape # endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth # configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in # Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside # the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the # <kubernetes_sd_config>. tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt # If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the # master CA, then you need to disable certificate verification. Note that # certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure # so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can # enable certificate verification by commenting the line below. # insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token # Keep only the default/kubernetes service endpoints for the https port. This # will add targets for each API server which Kubernetes adds an endpoint to # the default/kubernetes service. relabel_configs: - source_labels: [ __meta_kubernetes_namespace, __meta_kubernetes_service_name, __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name, ] action: keep regex: default;kubernetes;https - job_name: "kubernetes-nodes" # Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to # `http`. scheme: https # This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape # endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth # configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in # Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside # the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the # <kubernetes_sd_config>. tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt # If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the # master CA, then you need to disable certificate verification. Note that # certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure # so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can # enable certificate verification by commenting the line below. # insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+) - target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+) target_label: __metrics_path__ replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics - job_name: "kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor" # Default to scraping over https. If required, just disable this or change to # `http`. scheme: https # This TLS & bearer token file config is used to connect to the actual scrape # endpoints for cluster components. This is separate to discovery auth # configuration because discovery & scraping are two separate concerns in # Prometheus. The discovery auth config is automatic if Prometheus runs inside # the cluster. Otherwise, more config options have to be provided within the # <kubernetes_sd_config>. tls_config: ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt # If your node certificates are self-signed or use a different CA to the # master CA, then you need to disable certificate verification. Note that # certificate verification is an integral part of a secure infrastructure # so this should only be disabled in a controlled environment. You can # enable certificate verification by commenting the line below. # insecure_skip_verify: true bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: node # This configuration will work only on kubelet 1.7.3+ # As the scrape endpoints for cAdvisor have changed # if you are using older version you need to change the replacement to # replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1:4194/proxy/metrics # more info here https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator/issues/633 relabel_configs: - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+) - target_label: __address__ replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443 - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_node_name] regex: (.+) target_label: __metrics_path__ replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor # ignore timestamps of cadvisor's metrics by default # more info here https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/VictoriaMetrics/issues/4697#issuecomment-1656540535 honor_timestamps: false # Scrape config for service endpoints. # # The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured # via the following annotations: # # * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape services that have a value of `true` # * `prometheus.io/scheme`: If the metrics endpoint is secured then you will need # to set this to `https` & most likely set the `tls_config` of the scrape config. # * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this. # * `prometheus.io/port`: If the metrics are exposed on a different port to the # service then set this appropriately. # - job_name: "kubernetes-service-endpoints" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslices relabel_configs: - action: drop source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init] regex: true - action: keep_if_equal source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number] - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) - source_labels: [ __address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port, ] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] target_label: pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name] target_label: container - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: job replacement: ${1} - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] action: replace target_label: node # Scrape config for slow service endpoints; same as above, but with a larger # timeout and a larger interval # # The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured # via the following annotations: # # * `prometheus.io/scrape-slow`: Only scrape services that have a value of `true` # * `prometheus.io/scheme`: If the metrics endpoint is secured then you will need # to set this to `https` & most likely set the `tls_config` of the scrape config. # * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this. # * `prometheus.io/port`: If the metrics are exposed on a different port to the # service then set this appropriately. # - job_name: "kubernetes-service-endpoints-slow" scrape_interval: 5m scrape_timeout: 30s kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: endpointslices relabel_configs: - action: drop source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init] regex: true - action: keep_if_equal source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number] - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow] action: keep regex: true - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme] action: replace target_label: __scheme__ regex: (https?) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) - source_labels: [ __address__, __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port, ] action: replace target_label: __address__ regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] target_label: pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name] target_label: container - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: job replacement: ${1} - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] action: replace target_label: node # Example scrape config for probing services via the Blackbox Exporter. # # The relabeling allows the actual service scrape endpoint to be configured # via the following annotations: # # * `prometheus.io/probe`: Only probe services that have a value of `true` # - job_name: "kubernetes-services" metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: service relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe] action: keep regex: true - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target - target_label: __address__ replacement: blackbox - source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_service_name] target_label: service # Example scrape config for pods # # The relabeling allows the actual pod scrape endpoint to be configured via the # following annotations: # # * `prometheus.io/scrape`: Only scrape pods that have a value of `true` # * `prometheus.io/path`: If the metrics path is not `/metrics` override this. # * `prometheus.io/port`: Scrape the pod on the indicated port instead of the default of `9102`. # - job_name: "kubernetes-pods" kubernetes_sd_configs: - role: pod relabel_configs: - action: drop source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init] regex: true - action: keep_if_equal source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number] - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape] action: keep regex: true - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path] action: replace target_label: __metrics_path__ regex: (.+) - source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port] action: replace regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+) replacement: $1:$2 target_label: __address__ - action: labelmap regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+) - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name] target_label: pod - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name] target_label: container - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace] target_label: namespace - source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name] action: replace target_label: node ## End of COPY # -- Extra scrape configs that will be appended to `config` extraScrapeConfigs: [] probe: # -- Readiness probe readiness: httpGet: {} initialDelaySeconds: 5 periodSeconds: 15 # -- Liveness probe liveness: tcpSocket: {} initialDelaySeconds: 5 periodSeconds: 15 timeoutSeconds: 5 # -- Startup probe startup: {} # -- Add extra specs dynamically to this chart extraObjects: [] allowedMetricsEndpoints: - /metrics # -- Enterprise license key configuration for VictoriaMetrics enterprise. # Required only for VictoriaMetrics enterprise. Check docs [here](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/victoriametrics/enterprise/), # for more information, visit [site](https://victoriametrics.com/products/enterprise/). # Request a trial license [here](https://victoriametrics.com/products/enterprise/trial/) # Supported starting from VictoriaMetrics v1.94.0 license: # -- License key key: "" # -- Use existing secret with license key secret: # -- Existing secret name name: "" # -- Key in secret with license key key: "" -
Запустите установку ВМ-агента.
По завершению установки ВМ-агента перейдите к проверке успешности подключения кластера к Cloudmaster.
Проверка успешности подключения кластера⚓︎
-
В логах пода ВМ-агента проверьте, что агент обнаружил targets и в логах нет ошибок отправки данных.
-
В интерфейсе ВМ-агента VictoriaMetrics проверьте наличие targets:
Ниже приведена команда для пробрасывания порта пода. Предварительно нужно получить ID пода.
Список и активность по targets будет доступна по адресу http://localhost:8429/targets. Среди targets должны быть:kubectl get pods -n cloudmaster-vm -l app.kubernetes.io/name=victoria-metrics-agent kubectl port-forward pod/vmagent-victoria-metrics-agent-XXXXXXXXX 8429:8429 -n cloudmaster-vmkube-state-metrics,node-exporter,kubernetes-apiservers,kubernetes-nodes,kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor,kubernetes-service-endpoints. -
Проверьте подгрузку данных о
кластерев разделах Cloudmaster:-
информации о
подключениив подразделе Мои подключения , -
затраты по
кластерув разделе Kubernetes
-
Ошибка сбора метрик⚓︎
Если после выполнения всех действий по настройке сбора метрик в кластере подключение находится в состоянии Ошибка сбора метрик:
- Наведите курсор на карточку подключения и кликните на ,
- Кликните на Узнать об ошибке.
Появится модальное окно со статусом сбора метрик. Вам будет необходимо проверить наличие необходимых сервисов в кластере и корректность примененных yaml-файлов.